Heated floors offer a blend of comfort and efficiency, transforming cold floors into sources of soothing warmth and enhancing overall energy efficiency. This article explores the various benefits and drawbacks of heated floors, including their cost implications and compatibility with different flooring types. It also provides insights into key considerations for installation and the two primary types of systems—electric and hydronic—helping you determine the best option for your home.
By examining the pros and cons, along with factors such as budget, installation complexity, and system compatibility, this article aims to guide you in making an informed decision about whether heated floors are a worthwhile investment for your living space.
Two Main Types of Heated Floor Systems
The two main types of heated floor systems are electric radiant floor heating and hydronic radiant floor heating. Both systems offer distinct benefits and are suitable for different applications based on factors like budget, home size, and heating requirements.
Electric Radiant Floor Heating
This type uses electric cables or mats installed beneath the flooring to generate heat. This system is ideal for smaller areas like bathrooms or kitchens, where quick and direct warmth is desired. Electric systems are generally easier and faster to install, and they provide precise temperature control. However, they can be more expensive to operate, especially in larger spaces, due to the cost of electricity.

Hydronic Radiant Floor Heating
This involves circulating hot water through a network of tubes installed under the floor. This type of system is more energy-efficient for larger areas or whole-home heating, as it can be powered by various energy sources like gas, solar, or geothermal.
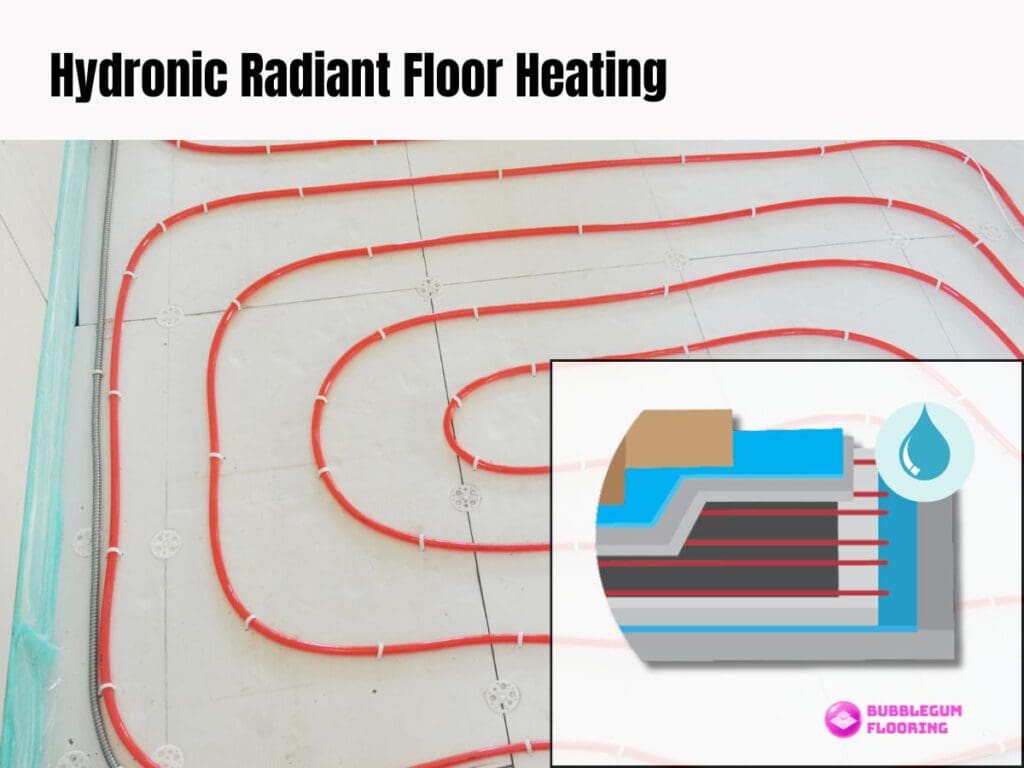
While hydronic systems offer consistent, long-lasting warmth and are more cost-effective over time, they require a more complex and costly installation process, including a boiler and extensive plumbing.
Both systems offer comfortable, consistent warmth, but the choice depends on factors such as the size of the area to be heated, the desired heating method, and installation preferences.
Pros of Installing Heated Floors
Radiant floor heating has become a popular home improvement option, known for its ability to enhance comfort while offering energy efficiency. Whether used in a single room or throughout the home, heated floors provide a cozy, even warmth that can be both luxurious and practical. Below are some of the key benefits of installing heated floors.
Comfort
Heated floors offer a gentle, consistent warmth from the ground up, which can be more soothing compared to the hot air produced by radiators or forced-air systems. This even warmth reduces the cold spots and drafts that can occur with other heating methods. It also means that rooms maintain a stable temperature, which can be particularly comforting on chilly mornings or in colder climates.
Energy Efficiency
Radiant floor heating systems are generally more energy-efficient because they operate at lower temperatures compared to traditional heating systems. They heat the floor and, in turn, the room from the ground up. This means they often use less energy to achieve and maintain a comfortable temperature. Additionally, because the heat is distributed evenly, there’s less need to overheat the space to make it comfortable, leading to potential cost savings on energy bills.
Even Heat Distribution
Traditional heating systems can create uneven temperatures in a room. For instance, radiators might make the area around them very warm while other parts of the room remain cool. In contrast, heated floors provide a uniform heat distribution. This is especially useful in larger rooms or open-plan spaces where maintaining consistent temperature can be challenging.
Improved Air Quality
Since heated floors don’t rely on air movement to distribute heat, they avoid the issue of stirring up dust and allergens that can happen with forced-air systems. This is beneficial for individuals with allergies or respiratory issues, as it helps maintain cleaner air and reduces potential irritants.
Design Flexibility
Without the need for bulky radiators, baseboards, or vents, you have more freedom in your interior design. You can place furniture and decor without worrying about obstructing heat sources. This can make a space look cleaner and more modern, with fewer obstructions and a more streamlined appearance.
Increased Property Value
Homes with modern and efficient features like heated floors can be more appealing to buyers. They represent a desirable upgrade, which can enhance the overall value of your property and make it stand out in the real estate market.
Low Maintenance
Heated floors have few moving parts and require little maintenance compared to other heating systems. There are no filters to change or mechanical components that might fail. Regular checks to ensure everything is functioning properly are usually all that’s needed.
Reduced Noise
Traditional heating systems can be noisy as they turn on and off or as air moves through ducts. Radiant floor heating operates silently, contributing to a quieter home environment. This can be particularly beneficial in bedrooms or quiet spaces where noise disruption is a concern.
Design Integration
Radiant floor heating can be installed under various types of flooring, including tile, stone, laminate, and engineered wood. This flexibility allows you to choose the flooring that best suits your design preferences without worrying about compatibility with your heating system.
While the initial installation cost may be higher, the long-term advantages can make radiant floor heating a worthwhile investment for homeowners looking to add warmth and value to their homes.
Cons of Installing Heated Floors
While heated floors offer numerous benefits, they are not without their drawbacks. Understanding these potential downsides can help you make a well-informed decision about whether this upgrade is right for your home. Here’s a look at some of the challenges associated with installing heated floors.
High Installation Costs
Heated floors can be expensive to install, especially in existing homes where retrofitting may involve lifting and replacing flooring. The cost of materials and labor can add up, making it a significant upfront investment.
Extended Installation Time
Installation can be time-consuming, especially for hydronic (water-based) systems, as they require significant groundwork. It often involves skilled labor and may disrupt daily life for several days during the installation process.
Floor Height Issues
Heated floor systems, particularly electric or hydronic types, can slightly raise the floor height, which may cause issues with doors, baseboards, or transitions between rooms. This can necessitate additional modifications to fit the system seamlessly.
Limited Compatibility with Some Floor Types
Certain flooring materials, like solid hardwood or thick carpets, may not work as well with heated floors. These materials can reduce the heat transfer and efficiency of the system, limiting the effectiveness of radiant heating.
Repair Complexity
If a problem arises, repairs can be complicated and costly since the heating system is embedded beneath the floor. Identifying and fixing issues often requires tearing up the flooring, leading to disruption and added expenses.
Slow Heating Response Time
Heated floors, particularly hydronic systems, can take longer to reach the desired temperature compared to traditional heating methods. This slow response time might not be ideal for those who need quick heating adjustments.
Evaluating these drawbacks in the context of your budget, home design, and heating needs will help you determine if radiant floor heating is the right choice for you.
Factors to Consider Before Deciding to Install Heated Floors
Heated floors can add significant comfort and efficiency to your home, but deciding whether to install them requires careful consideration of several factors. Here’s what you need to think about before making this investment:
Budget
Evaluate both the initial cost of installation and long-term energy savings. While heated floors can be more energy-efficient, the upfront costs, including materials, labor, and potential retrofitting expenses, can be significant. Factor in your budget to determine whether the long-term savings justify the initial investment.
Type of System (Electric vs. Hydronic)
Electric systems are generally easier and less costly to install but can be more expensive to run, making them ideal for smaller areas like bathrooms. Hydronic (water-based) systems are more efficient for large spaces and entire homes, but they are more complex to install and may require additional infrastructure like a boiler.
Flooring Compatibility
Not all flooring materials work well with radiant heating. Tile, stone, and concrete are the best heat conductors, while materials like hardwood or thick carpets can reduce heat transfer. Make sure your preferred flooring type aligns with the heating system for optimal efficiency.
Energy Source
Consider the energy source that will power the system. Electric systems rely on electricity, which can be costly depending on your local rates. Hydronic systems, on the other hand, often use gas or other energy-efficient sources like solar or geothermal, which may offer long-term savings but require more complex installation.
Home Layout and Usage
If you’re only heating certain rooms (like bathrooms or kitchens), electric systems may be sufficient. For larger areas or whole-home installations, hydronic systems could be more cost-effective. Also, consider how often you use certain spaces to ensure the investment is worth it.
Installation Time and Disruption
Installing heated floors can be disruptive, especially in existing homes. Be prepared for potential delays, the need to move furniture, and even the possibility of having to stay elsewhere during installation.
Climate
The effectiveness of heated floors can vary depending on your local climate. In colder climates, they can be a valuable heating source, while in milder areas, they may be more of a luxury than a necessity.
Maintenance and Repairs
Consider the long-term maintenance needs of your system. While heated floors generally require little upkeep, repairs can be costly and disruptive, especially if the system is embedded in the floor. Ensure you’re prepared for potential repair complexities.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
If sustainability is important to you, look for energy-efficient options such as solar-powered hydronic systems or systems that integrate well with energy-saving technologies. This can lower both your carbon footprint and long-term costs.
By carefully considering these aspects, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your home’s needs and your personal comfort preferences. If the benefits of radiant heating meet your requirements and you’re prepared for investment and maintenance, heated floors can be a valuable upgrade to enhance your home’s warmth and efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, heated floor systems offer significant benefits, including consistent warmth, enhanced comfort, and improved energy efficiency. These systems can elevate your home’s comfort level and air quality, making them a desirable feature for many. However, they also come with potential drawbacks, such as high installation costs, possible compatibility issues with certain flooring types, and varying energy efficiency depending on the system chosen.
When considering heated floors, it’s crucial to evaluate factors such as your budget, the type of system that best suits your needs (electric or hydronic), and how well it integrates with your current flooring. By weighing these aspects, you can make an informed decision about whether heated floors are a practical and worthwhile investment for your home.


